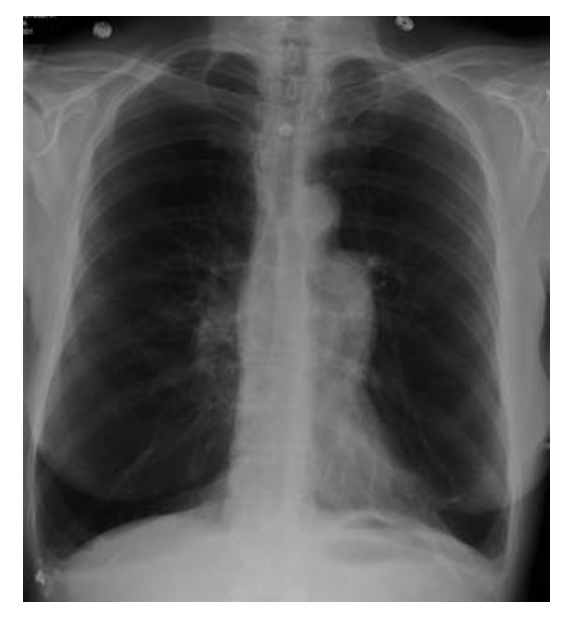
A 45-year-old white woman presents to her physician complaining of several months of worsening shortness of breath. Previously she was told she had asthma because she was hav- ing intermittent episodes of wheezing com- bined with a productive cough and difficulty catching her breath. She used to run two miles every morning but can no longer walk more than 10 city blocks without stopping. She has never smoked. On physical examination she is using her accessory muscles to assist with res- piration. Pulmonary examination is notable for an increased decreased FEV1/FVC ratio, decreased air movement with each breath, and increased resonance upon percussion. X-ray of the chest is shown in the image. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause for this patient’s disease?
-
(A) A genetic mutation resulting in deficient levels of a protease
-
(B) A genetic mutation resulting in deficient levels of a protease inhibitor
-
(C) A mutation in the p53 gene
-
(D) A mutation of the CFTR gene, which en-
codes a regulated chloride channel
-
(E) Airway inflammation, airflow obstruction,
and bronchial hyperresponsiveness